Introduction
Smoking is one of the most common and harmful habits that millions of people around the world engage in. Smoking can cause various health problems, such as lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). One of the most noticeable and annoying effects of smoking is the cough that smokers often develop. But why does smoking make us cough? What is the science behind the smoke?
The Anatomy of the Respiratory System
To understand why smoking makes us cough, we need to first understand how the respiratory system works. The respiratory system consists of the nose, mouth, throat, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. These organs and structures work together to deliver oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the body.
The nose and mouth are the entry points for air into the respiratory system. The air then passes through the throat and the larynx, which is also known as the voice box. The larynx contains the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound. The air then enters the trachea, which is also known as the windpipe. The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi.
The bronchi are two branches of the trachea that split into smaller tubes called bronchioles. The bronchioles further divide into tiny air sacs called alveoli. The alveoli are the site of gas exchange, where oxygen from the air diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the air. The alveoli are surrounded by a network of capillaries, which are small blood vessels that transport blood to and from the lungs.
The respiratory system also has a protective mechanism to prevent foreign particles and pathogens from entering the lungs. The nose and mouth have hairs and mucus that trap dust, pollen, bacteria, and viruses. The throat and the larynx have cilia, which are tiny hair-like structures that move in a wave-like motion to sweep mucus and debris upward. The trachea and the bronchi also have cilia and mucus that perform the same function. The mucus and the debris are then either swallowed or spit out.

The Effects of Smoking on the Respiratory System
When a person smokes, they inhale a mixture of gases and particles that are produced by the burning of tobacco and other substances. Some of the harmful components of cigarette smoke are:
Nicotine:
A highly addictive substance that stimulates the nervous system and increases blood pressure and heart rate.
Tar:
A sticky substance that coats the lungs and contains carcinogens, which are substances that can cause cancer.
Carbon monoxide:
A poisonous gas that reduces the amount of oxygen that the blood can carry.
Formaldehyde:
A chemical that can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs and can cause cancer.
Hydrogen cyanide:
A toxic gas that can damage the cilia and impair their function.
Acetone:
A solvent that can dry out the mucous membranes and cause inflammation.
Ammonia:
A compound that can irritate the respiratory tract and increase mucus production.
These and other components of cigarette smoke can damage the respiratory system in various ways, such as:
- Reducing the amount of oxygen that reaches the lungs and the tissues, leads to hypoxia, which is a condition of low oxygen levels.
- Increasing the risk of infections, such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and tuberculosis, by weakening the immune system and impairing the cilia and mucus function.
- Causing inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to wheezing, shortness of breath, and asthma.
- Destroying the alveoli and reducing the surface area for gas exchange, leads to emphysema, which is a condition of lung damage and reduced lung function.
- Stimulating the production of mucus and increasing its viscosity, leads to chronic bronchitis, which is a condition of persistent cough and mucus production.
- This causes abnormal cell growth and mutations, leading to lung cancer, which is a condition of uncontrolled cell division and tumor formation.
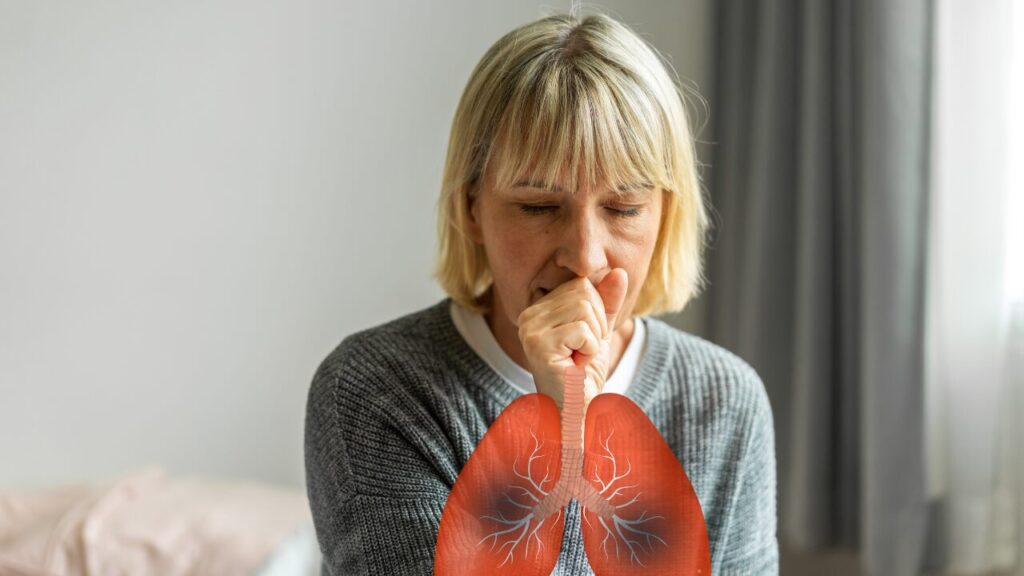
The Mechanism of the Smoker’s Cough
The smoker’s cough is a result of the damage and irritation caused by cigarette smoke to the respiratory system. The smoker’s cough can be classified into two types:
Acute cough:
This is the cough that occurs immediately after smoking or during smoking. This is caused by the irritation of the throat, the larynx, and the trachea by the hot and dry smoke. This cough is usually dry and harsh and lasts for a few seconds or minutes.
Chronic cough:
This is the cough that persists for a long time, even after quitting smoking. This is caused by the inflammation and mucus accumulation in the bronchi and the bronchioles. This cough is usually productive and brings up phlegm that may be yellow, green, or brown. This cough may last for months or years and may worsen in the morning or at night.
The smoker’s cough is a reflex action that is triggered by the stimulation of the cough receptors in the respiratory tract. The cough receptors are nerve endings that sense the presence of foreign particles, mucus, or irritants in the airways. When the cough receptors are stimulated, they send signals to the brain, which then activates the cough center in the medulla oblongata. The cough center then sends signals to the muscles involved in coughing, such as the diaphragm, the intercostal muscles, the abdominal muscles, and the laryngeal muscles. These muscles contract and relax in a coordinated manner to create a high-pressure airflow that expels the foreign particles, mucus, or irritants from the lungs.
The smoker’s cough is a way for the body to try to clear the lungs of the harmful substances that are present in cigarette smoke. However, the smoker’s cough is not effective in removing all the toxins and carcinogens from the lungs. Moreover, the smoker’s cough can cause further damage and irritation to the respiratory system, leading to more inflammation, mucus production, and coughing. This creates a vicious cycle that can worsen the condition of the lungs and increase the risk of serious diseases.
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking
The best way to prevent and treat the smoker’s cough is to quit smoking. Quitting smoking can have immediate and long-term benefits for the respiratory system and overall health. Some of the benefits of quitting smoking are:
- Within 20 minutes of quitting smoking, the blood pressure and the heart rate return to normal levels.
- Within 8 hours of quitting smoking, the carbon monoxide levels in the blood drop and the oxygen levels increase.
- Within 24 hours of quitting smoking, the risk of heart attack decreases.
- Within 48 hours of quitting smoking, the sense of smell and taste improves.
- Within 72 hours of quitting smoking, the bronchial tubes relax and the breathing becomes easier.
- Within 2 weeks to 3 months of quitting smoking, the blood circulation improves and the lung function increases by up to 30%.
- Within 1 to 9 months of quitting smoking, the cilia and mucus function recover, and the coughing and wheezing decrease.
- Within 1 year of quitting smoking, the risk of coronary heart disease is reduced by half.
- Within 5 years of quitting smoking, the risk of stroke is reduced to that of a non-smoker.
- Within 10 years of quitting smoking, the risk of lung cancer is reduced by half and the risk of other cancers, such as mouth, throat, esophagus, bladder, kidney, and pancreas, is also reduced.
- Within 15 years of quitting smoking, the risk of coronary heart disease is equal to that of a non-smoker.
Quitting smoking can also improve the appearance, the mood, the energy, the confidence, and the quality of life of the former smoker. Quitting smoking can also save money, time, and resources that would otherwise be spent on cigarettes and smoking-related diseases.

The Tips for Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking can be challenging, but it is possible with the right motivation, support, and strategies. Some of the tips for quitting smoking are:
- Set a quit date and stick to it. Choose a day that is not too stressful or busy and mark it on the calendar.
- Make a list of the reasons for quitting smoking and keep it handy. Review the list whenever the urge to smoke arises and remind yourself of the benefits of quitting smoking.
- Seek support from family, friends, co-workers, or health professionals. Tell them about your quit plan and ask them to help you stay on track. Join a quit-smoking program or a support group to get advice and encouragement from other people who are trying to quit smoking or have successfully quit smoking.
- Use nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) or medication to ease the withdrawal symptoms and cravings. NRT products, such as patches, gums, lozenges, inhalers, or sprays, deliver a controlled dose of nicotine to the body without the harmful chemicals of cigarette smoke. Medications, such as bupropion or varenicline, work by affecting the brain receptors that are involved in nicotine addiction. Consult a doctor before using NRT or medication and follow the instructions carefully.
- Avoid triggers and temptations that may make you want to smoke. Triggers can be people, places, situations, or emotions that are associated with smoking. Temptations can be cigarettes, lighters, ashtrays, or other smoking paraphernalia. Identify your triggers and temptations and plan how to cope with them. For example, you can avoid smokers or smoking areas, use a different route to work or school, drink water or chew gum instead of smoking, distract yourself with a hobby or a task, or call a friend or a helpline when you feel stressed or anxious
- Reward yourself for your achievements and celebrate your milestones. Quitting smoking is a big accomplishment and you deserve to be proud of yourself. Treat yourself to something you enjoy, such as a movie, a book, a game, or a meal. Share your success with your loved ones and thank them for their support.
- Be prepared for relapses and setbacks and do not give up. Quitting smoking is not easy and it may take several attempts to quit for good. If you slip up and smoke a cigarette, do not feel guilty or discouraged. Learn from your mistake and identify what triggered you to smoke. Make a plan to avoid or cope with that trigger in the future. Remind yourself of your reasons and benefits for quitting smoking and resume your quit plan as soon as possible.
- Quitting smoking is one of the best decisions you can make for your health and well-being. By quitting smoking, you can improve your respiratory system and reduce the risk of the smoker’s cough and other serious diseases. You can also enhance your appearance, your mood, your energy, your confidence, and your quality of life. Quitting smoking can be challenging, but it is possible with the right motivation, support, and strategies. You can do it!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about smoking and coughing.
The duration of a smoker’s cough after quitting smoking varies from person to person. Some people may stop coughing within a few weeks, while others may continue to cough for several months or even years. The factors that affect the duration of smoker’s cough include the length and intensity of smoking history, the degree of lung damage, the presence of other lung conditions, and the overall health and lifestyle of the former smoker.
The best way to relieve a smoker’s cough is to quit smoking. However, there are some home remedies and over-the-counter medications that may help ease the symptoms of a smoker’s cough. These include:
1. Drink plenty of fluids to thin the mucus and keep the throat moist.
2. Using a humidifier or a vaporizer to add moisture to the air and soothe the airways.
3. Gargling with warm salt water to reduce inflammation and infection in the throat.
4. Take honey or lozenges to coat and calm the throat.
5. Taking cough suppressants or expectorants to reduce or loosen the phlegm.
6. Taking anti-inflammatory or pain relievers to reduce swelling and discomfort in the chest.
7. Avoid irritants and allergens that may trigger or worsen the cough, such as dust, smoke, pollen, or perfume.
Smoking can cause various lung problems that may be life-threatening, such as lung cancer, COPD, or pneumonia. Some of the signs of a serious lung problem caused by smoking are:
1. Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum.
2. Having chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing.
3. Having difficulty breathing or shortness of breath that interferes with daily activities.
4. Having unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite, or fatigue.
5. Having recurrent or persistent lung infections, such as bronchitis or pneumonia.
6. Having a change in the voice or hoarseness.
7. Having a new or changing lump or mass in the neck or face.
If you have any of these signs, you should see your doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Smoking is one of the most common and harmful habits that millions of people around the world engage in. Smoking can cause various health problems, such as lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). One of the most noticeable and annoying effects of smoking is the cough that smokers often develop. Smoking damages the respiratory system in various ways, such as reducing the oxygen levels, increasing the risk of infections, causing inflammation and narrowing of the airways, destroying the alveoli, stimulating the production of mucus, and causing abnormal cell growth and mutations. Smoking also affects the natural mechanism of the body to clear the lungs of the harmful substances, such as the cilia and the mucus. The smoker’s cough is a reflex action that is triggered by the stimulation of the cough receptors in the respiratory tract. The smoker’s cough is a way of the body to try to clear the lungs of the toxins and carcinogens that are present in cigarette smoke. However, the smoker’s cough is not effective in removing all the toxins and carcinogens from the lungs. Moreover, the smoker’s cough can cause further damage and irritation to the respiratory system, leading to more inflammation, mucus production, and coughing. This creates a vicious cycle that can worsen the condition of the lungs and increase the risk of serious diseases. The best way to prevent and treat the smoker’s cough is to quit smoking. Quitting smoking can have immediate and long-term benefits for the respiratory system and overall health. Quitting smoking can improve oxygen levels, reduce the risk of infections, ease the inflammation and narrowing of the airways, restore the alveoli, decrease mucus production, and lower the risk of cancer. Quitting smoking can also improve the appearance, mood, energy, confidence, and quality of life of the former smoker. Quitting smoking can be challenging, but it is possible with the right motivation, support, and strategies. Some of the tips for quitting smoking are setting a quit date, making a list of the reasons for quitting, seeking support, using nicotine replacement therapy or medication, avoiding triggers and temptations, rewarding yourself, and being prepared for relapses and setbacks. Quitting smoking is one of the best decisions you can make for your health and well-being. By quitting smoking, you can improve your respiratory system and reduce the risk of the smoker’s cough and other serious diseases. You can also enhance your appearance, your mood, your energy, your confidence, and your quality of life. Quitting smoking can be challenging, but it is possible with the right motivation, support, and strategies. You can do it!
Also note that, sometimes this cough gets worse in the morning. Why? Because during sleep. The cilia begin to repair themselves and start expelling the harmful substances.
Now, to remove all the harmful substances, our body starts coughing more in the morning.
I Hope You Like This Short Article For More Article Like This Please Follow us on Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube












